Bulging Disc vs Herniated Disc: Key Differences & Treatments
Spinal disc problems are a common cause of back pain and discomfort, affecting individuals of all ages. Two terms frequently used in diagnosing spine-related issues are “bulging disc” and “herniated disc.” While they might sound similar, these conditions differ in their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the distinction between a bulging disc and herniated disc is crucial for seeking appropriate care and relief.
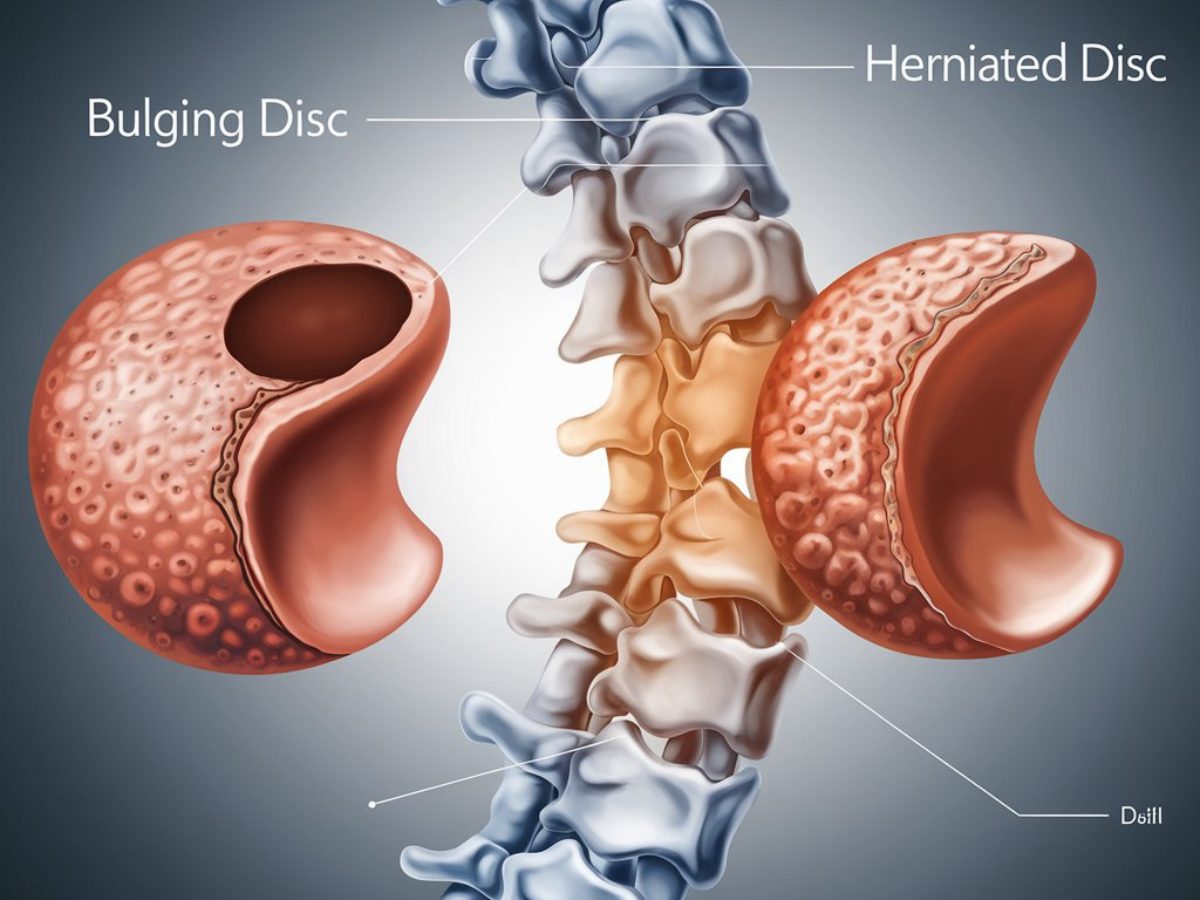
What Is a Bulging Disc?
A bulging disc occurs when the outer layer of a spinal disc protrudes beyond its normal boundary. Think of it as a deflated balloon that’s flattened on one side.
- Cause: A bulging disc is often a result of age-related wear and tear, also known as disc degeneration. Poor posture, repetitive stress, or prolonged sitting can also contribute.
- Symptoms: Most bulging discs are asymptomatic but may cause mild pain, stiffness, or discomfort if they compress nearby nerves.
- Location: Bulging discs often occur in the lumbar (lower back) or cervical (neck) regions.
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the inner gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) leaks through a tear in the outer layer (annulus fibrosus).
- Cause: Herniated discs are commonly caused by sudden injury, heavy lifting, or twisting motions.
- Symptoms: Unlike bulging discs, herniated discs frequently press on spinal nerves, causing sharp pain, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness.
- Location: Herniated discs are most common in the lower back and may lead to sciatica if they compress the sciatic nerve.
Diagnosis
Both conditions are diagnosed using imaging tests such as MRI, CT scans, or X-rays. A detailed physical exam and patient history help pinpoint the cause of symptoms.
Treatment Options
- Conservative Measures:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthens the muscles supporting the spine.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Proper posture, ergonomic adjustments, and weight management can alleviate symptoms.
- Injections:
- Epidural steroid injections may relieve pain by reducing inflammation around the affected nerve.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Surgery is rare for bulging discs but may be necessary for herniated discs causing persistent nerve compression.
Preventive Tips
- Maintain Good Posture: Sit and stand with proper alignment to minimize spinal stress.
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthen core and back muscles to support the spine.
- Lift Properly: Bend at your knees, not your waist, when lifting heavy objects.
- Stay Active: Prolonged sitting or inactivity can increase the risk of spinal disc issues.
How SBJI Can Help
At Sunshine Bone and Joint Institute, our multidisciplinary team specializes in diagnosing and treating spine conditions, including bulging and herniated discs. Using advanced imaging, individualized care plans, and state-of-the-art techniques, we ensure that every patient receives the most effective treatment for their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sharp pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs are common herniated disc symptoms.
Yes, a bulging disc can progress to a herniated disc if the outer layer weakens or tears.
Physical therapy, NSAIDs, lifestyle modifications, and occasionally steroid injections are effective non-surgical treatments.
Surgery may be necessary if symptoms persist despite conservative treatment or if there is severe nerve compression.
SBJI provides personalized care, offering advanced diagnostics, non-invasive therapies, and expert surgical interventions tailored to your needs.

