Bone Fractures: Common Symptoms, Treatment Methods, and Potential Risks
The term ‘fracture’ means a break in a structure- so when we talk about bone fractures, it is pretty self-explanatory. Bones are incredibly strong tissue that provide great structural integrity to the body but they are NOT indestructible. They need to be taken care of properly and they can break if there is an accident.
What Causes Bone Fractures?
Bones are strong and are made of a unique composition of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and other minerals, along with Vitamin D. But, they can break due to a variety of reasons, some of which have been discussed below-
- Accidental falls, slips in older folk or younger children can cause broken bones.
- For some people who have congenital bone defects or are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis and related conditions, taking care of their bones needs to be a priority.
- Older people with worn down joints and bones are at a greater risk of fracturing their bones- the hips, knees or wrists are especially vulnerable.
- High impact sports like football, wrestling, skiing, gymnastics etc. carry a greater risk of injury for children too.
- People who have bone cancer or infections can have weak bones, which can cause fractures more easily.
- Lastly, physical assault or abuse of any kind can also cause broken bones.
Types Of Bone Fractures
Fractures have been classified into different types depending on where bones break, how severe it is and what kind of treatment is needed to make it heal. Some common kinds have been explained in greater detail below:
The different types of fractures that you need to know of are-
-
Spiral fracture: Normally occurs when bones have been twisted. Seen in accidents or situations of abuse or even sports injuries.
-
Transverse fracture: The bone breaks perpendicular to its long axis, if enough force is applied.
-
Stress fracture: Repetitive actions can affect both joints and bones due to increased wear and tear. They are also seen in athletes – especially in the weight bearing bones like the metatarsals or tibia.
-
Compression fracture: These fractures affect the spine and can cause intense pain and change in posture and other issues if not treated immediately. These bones can break due to age, osteoporosis or even trauma.
-
Greenstick Fracture: Common in kids, the bones can break more easily as they are not hard or mature enough. Since their bones have more collagen, the bone will bend more easily, but will break only a little. This resembles a young green stick, which is not easy to break, but will still bend if enough pressure is applied.
-
Impacted fracture: One piece of the broken bone gets jammed into another piece of the bone. This is caused due to collision or traumatic accidents. Falls can also do this, but rarely.
-
Oblique Fracture: The bone breaks across the bone shaft if enough force is applied. It is due to axial compression and bending occurring at the same time.
-
Comminuted fracture: If the bone breaks into 3 or more fragments due to a bad fall or an accident, then healing takes time.
-
Linear Fracture: The bone fracture is along the long axis of the bone and is in a straight line, which means it will heal well without too much external treatment, provided it is kept immobile and all other conditions are met.
-
Segmental Fracture: If there are more than 2 breaks or cracks in the bone in different places, then there is more bone instability than usual.
Bone Fracture Symptoms
The symptoms of a broken bone will depend on how many breaks there are, how it happened and other related factors. Some common symptoms include-
- Pain and swelling at the site of the break.
- You may notice a deformity or the bone protruding out at an odd angle.
- You may be in extreme pain and can move the affected limb a bit or you won’t be able to move it at all.
- The area of the fracture may feel very tender and red.
- You may have to deal with numbness or tingling in some cases due to the nerves getting affected.
- Another bone may rub against the affected bone, leading to a popping sound (called crepitus).
- If the skin barrier has been breached, then you will be able to notice the bone jutting out. There is greater risk of infection in such cases.
But, hairline cracks may not be as painful, so please talk to your doctor and do NOT ignore any symptoms.
Treatment For Bone Fractures
Treatment mainly depends on whether the bone is broken in several places and associated pain and instability, activity level and general health of the patient.
- Bone fractures are generally treated by immobilising the joint- so that the body itself can heal without any issues. A brace, splint or traction device of some sort will be used in this regard.
- Affected bones can also undergo reduction if they are just misaligned. This can be done with or without surgery.
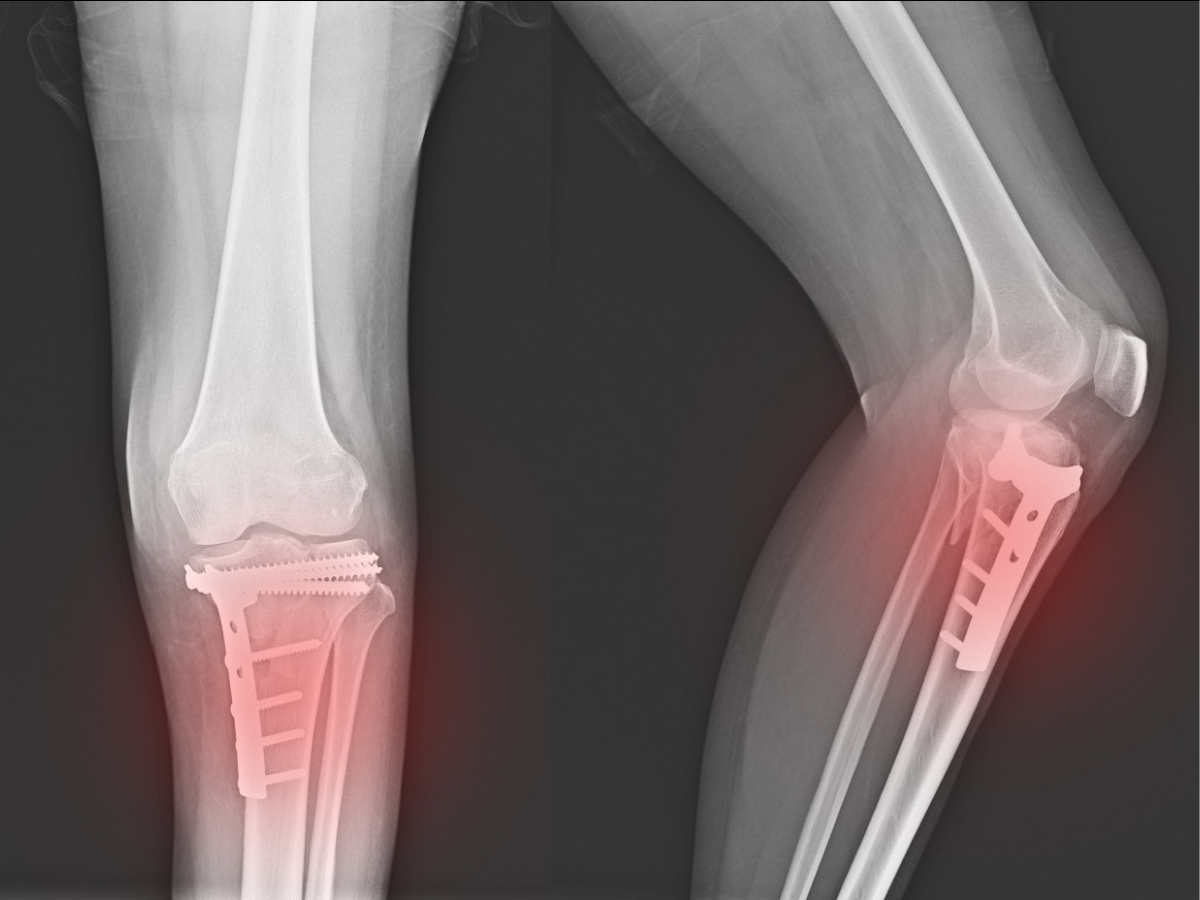
- Other orthopedic treatment for fractures can include surgery with insertion of rods, screws or plates to hold the bone in place, till it heals. It can then be removed afterwards, in most cases.
- Pain killers will be given to help you deal with the pain.
- You will need to undergo physical therapy as muscle loss and instability will be common after the cast or brace is removed.
Fractures heal definitely, but how they heal matters a lot- and getting timely orthopaedic treatment for fractures is super important. In general though, fractures take about 6-8 weeks to heal, though weight bearing bones may take much longer. So, if you are curious about fracture healing time, then remember that your body needs gentle love and care for it to heal.
Frequently Asked Questions
Typical symptoms include sudden pain, swelling, bruising, inability to move the affected limb, visible deformity, or a cracking sound at the time of injury. In severe cases, the broken bone may protrude through the skin.
Fractures are usually diagnosed using X-rays, which clearly show the location and type of break. In complex cases, CT scans or MRIs may be needed to assess soft tissue damage or more detailed bone structure.
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the fracture. Common methods include casting or splinting, traction, and surgical intervention (using pins, plates, or screws). Pain management and rehabilitation are also key components of recovery.
Healing time varies based on factors like age, overall health, bone involved, and severity of the break. Most fractures heal in 6–8 weeks, but some may take longer, especially in older adults or complex cases.
Complications can include infection (especially in open fractures), improper healing or non-union, nerve or blood vessel damage, chronic pain and reduced mobility. Early and appropriate treatment reduces the risk of long-term problems.

